Accounts Receivable (AR) represents outstanding payments owed to healthcare providers by patients or insurance companies. A decrease in AR typically signals efficient collection processes, indicating improved financial health. This post will cover the advantages of reduced AR, the formulas used in calculating AR, practical examples, and critical questions to deepen understanding.
Detailed Notes
Understanding Accounts Receivable in Healthcare
Definition of AR: Accounts Receivable represents the unpaid claims for services rendered, pending from insurance companies or patients.
Importance in Healthcare: In healthcare, AR reflects the amount owed, with a high AR indicating a lag in payment collection, which can stress a provider’s cash flow.
Formula to Calculate AR Turnover Ratio:
AR Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Average Accounts Receivable
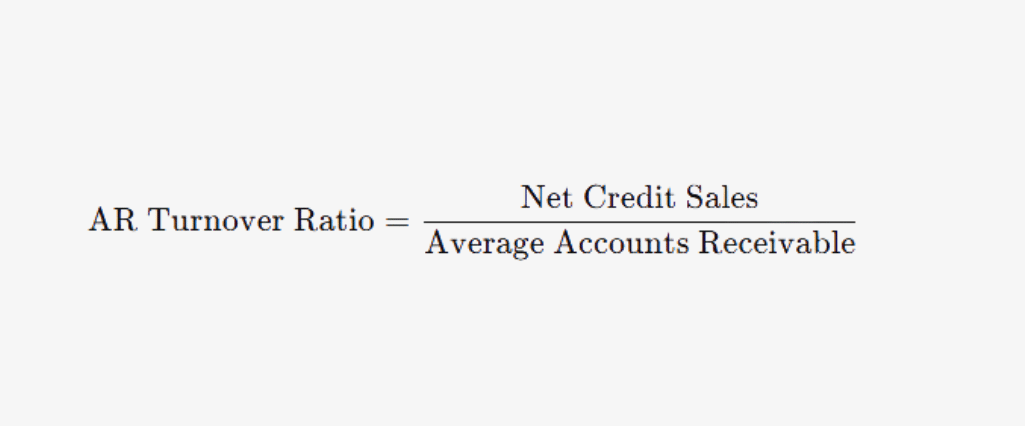
Example Calculation: If a healthcare provider has $500,000 in net credit sales and an average AR balance of $100,000: AR Turnover Ratio=500,000 / 100,000 = 5
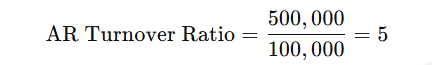
This means the provider collects its outstanding AR five times a year.
Benefits of Decreased AR for Healthcare Providers
A. Improved Cash Flow
Explanation: Lower AR means that funds are collected sooner, allowing providers to cover operational costs, invest in facilities, and handle emergencies without financial strain.
Key Metric: Days in AR (DAR)
Formula:
Days in AR=Ending AR BalanceTotal Credit Sales×365

Interpretation: A low DAR signifies quicker collection and better financial liquidity.
B. Faster Payment Cycles
- Explanation: Reduced AR implies streamlined billing processes and faster patient or insurance payments.
- Impact: Shorter payment cycles decrease the risk of bad debts and enable the provider to reallocate resources to other areas, like patient care or technology upgrades.
C. Enhanced Financial Health and Stability
- Explanation: Lower AR generally means fewer unpaid claims, indicating financial stability and potentially better creditworthiness.
- Indicators: A stable or improving AR turnover ratio suggests that the practice is effectively managing collections and minimizing outstanding dues.
Formulas and Calculations for Financial Metrics
Average Collection Period
Formula:
Average Collection Period = Accounts Receivable / Total Credit Sales × 365

Example Calculation: If AR is $150,000 and credit sales are $1,200,000, then:
Average Collection Period =150,0001,200,000×365=45.625 days
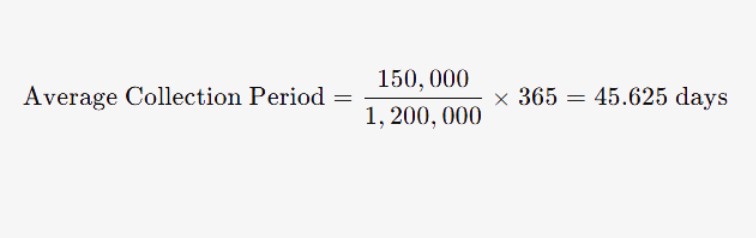
Interpretation: A lower collection period implies faster collections, positively impacting cash flow.
AR Aging Analysis
- Purpose: Categorizes AR based on the age of invoices (e.g., 0-30 days, 31-60 days).
- Impact: Helps providers identify overdue payments and take corrective action to maintain a low AR balance.
Key Takeaways Table
| Key Point | Explanation |
| Lower AR signals better cash flow | A decrease in AR indicates timely collections, allowing funds for operational needs and growth. |
| Faster payment cycles | Lower AR reflects efficient billing, reducing bad debt risk and supporting reinvestment in the practice. |
| Improved financial health | Reduced AR shows fewer unpaid claims, signaling financial stability and potentially increasing creditworthiness. |
Common Mistakes and Solutions
| Common Mistake | Solution |
| Ignoring AR aging analysis | Regularly categorize AR by invoice age to prioritize overdue collections. |
| Overlooking small overdue accounts | Small amounts can accumulate; track and follow up on all overdue accounts, no matter how minor. |
| Not calculating AR turnover regularly | Calculate AR turnover monthly or quarterly to track collection efficiency and identify any negative trends. |
Critical Thinking Questions
- How can reducing AR impact patient satisfaction and overall provider efficiency in healthcare?
- What factors might influence an increase in AR despite a provider’s efforts to improve collections?
- In what ways could a high AR turnover ratio support a healthcare provider’s expansion or investment plans?
This comprehensive structure should provide a clear understanding of how decreased AR benefits healthcare providers by enhancing cash flow, ensuring financial stability, and promoting faster collection cycles. Please let me know if you’d like to explore any of these aspects in further detail.
